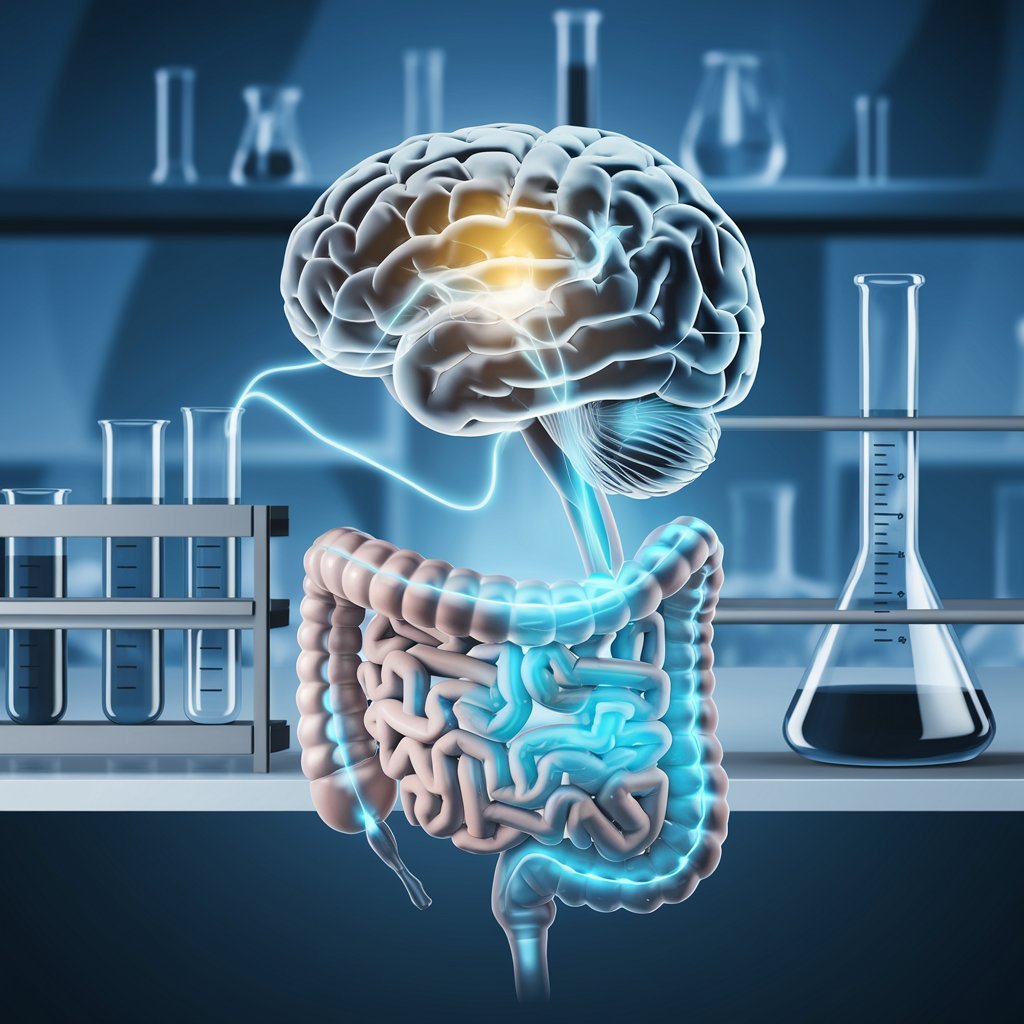
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Diet Impacts Mental Health – Explore the Science of Nutrition and Mood
Introduction
In recent years, research has unveiled the powerful link between our gut and our mental well-being—what scientists call the gut-brain connection. This discovery has shifted perspectives on mental health, recognizing that our digestive health can play a significant role in mood regulation, cognitive function, and even emotional resilience. Now, people are more eager than ever to understand how dietary choices impact mental health and to explore natural, nutrition-based ways to enhance well-being.
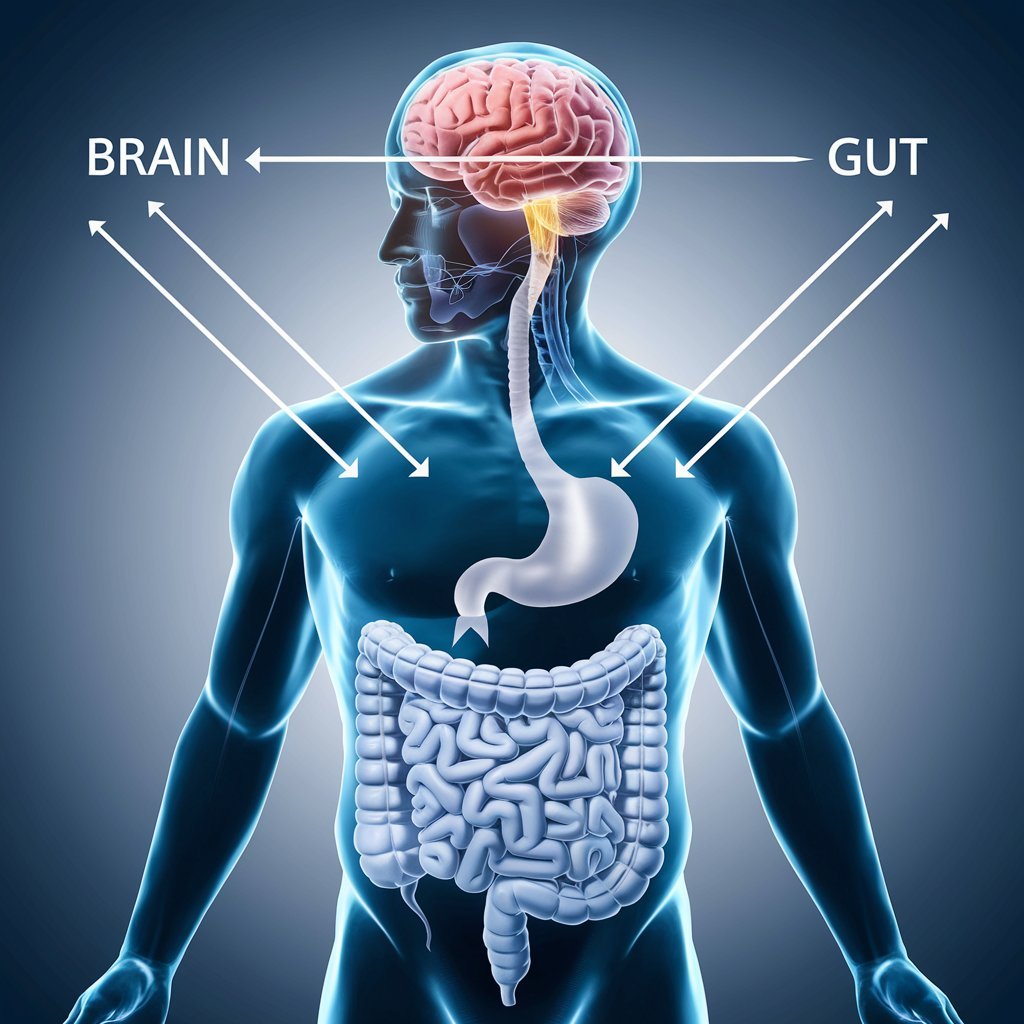
In this article, we’ll explore the science behind the gut-brain connection, how food choices impact mood, and the practical steps you can take to improve your mental health through diet. From probiotics to fiber-rich foods and specific dietary patterns, we’ll provide actionable tips to support your journey toward mental clarity and emotional wellness.
1. What Is the Gut-Brain Connection?
The gut-brain connection refers to the bidirectional communication between the digestive tract and the brain. This relationship is complex, involving physical pathways, chemical messengers, and a unique ecosystem of microorganisms known as the gut microbiome. In short, our brains and guts are constantly “talking,” influencing each other’s functions. Through the vagus nerve and biochemical messengers, the gut can impact brain activity, affecting mood, cognitive function, and even how we respond to stress.
Key Functions of the Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis plays several roles in mental health:
- Regulating Neurotransmitters: Certain gut bacteria produce or influence neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which help regulate mood.
- Controlling Inflammation: A balanced gut can reduce inflammation, which is often linked to conditions like depression and anxiety.
- Boosting Immunity: The gut microbiome supports immune functions that, when disrupted, can impact mental health.
A well-balanced gut leads to a balanced mind. Start prioritizing your gut health to help improve your mood and resilience to stress.
2. The Gut Microbiome: A Key Player in Mental Health
The gut microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that perform essential functions in digestion and immunity. However, recent studies have shown that a healthy microbiome is just as critical for mental well-being.
How Your Microbiome Impacts Mental Health
Research highlights several ways the gut microbiome affects mental health:
- Neurotransmitter Production: Around 90% of serotonin, often called the “happiness hormone,” is produced in the gut. Certain gut bacteria synthesize serotonin, influencing mood directly.
- Stress Response Regulation: Gut bacteria regulate cortisol levels, the stress hormone, affecting mood stability and stress resilience.
- Inflammation Reduction: A balanced microbiome reduces inflammation, while imbalances are linked to chronic inflammation, a factor in many mental health disorders.

When we think of mental health holistically, it becomes clear that a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for emotional stability and cognitive clarity.
3. How Diet Affects the Gut-Brain Connection
Our food choices directly impact the gut microbiome. Diets high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can create an imbalance in gut bacteria, called dysbiosis, which has been associated with higher rates of depression and anxiety. On the other hand, a nutrient-dense, fiber-rich diet can nurture beneficial bacteria, leading to positive mental health outcomes.
Foods That Benefit the Gut-Brain Connection
Here are some foods scientifically shown to support a healthy gut and brain:
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kombucha contain live bacteria that benefit the gut.
- Prebiotic Foods: High-fiber foods like bananas, garlic, onions, and asparagus feed good bacteria, promoting a balanced microbiome.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, omega-3s have anti-inflammatory effects that support brain health.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Blueberries, dark chocolate, and leafy greens protect brain cells from oxidative stress.
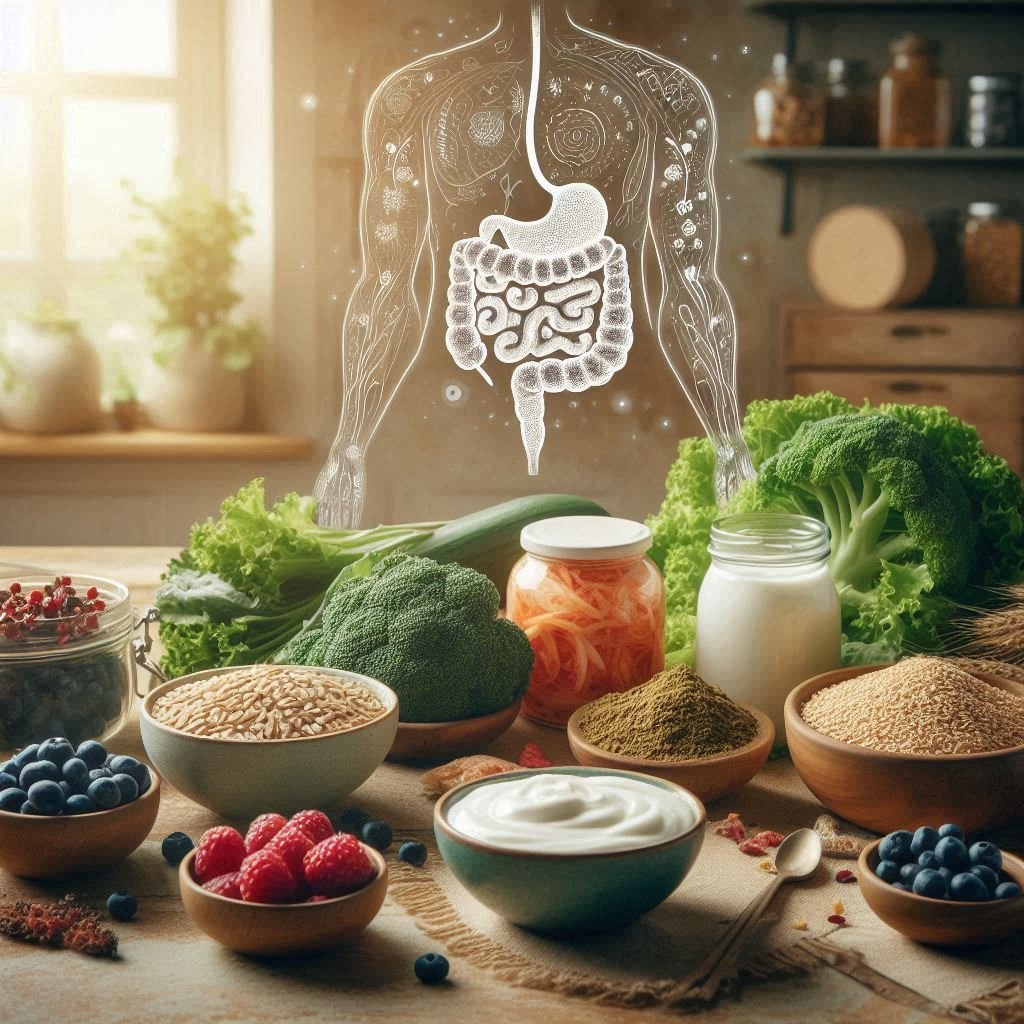

Eating nutrient-dense foods benefits not only physical health but mental clarity and emotional well-being. Consider incorporating more gut-friendly foods into your diet for better mental health.
4. The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in Mental Wellness
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help balance the gut microbiome, while prebiotics are fibers that feed these bacteria. Together, they maintain a healthy gut environment, which in turn supports neurotransmitter production, mood regulation, and mental health.
Benefits of Probiotics and Prebiotics for Mental Health
Research has shown that consuming probiotics and prebiotics can:
- Lower Anxiety and Depression Symptoms: Certain probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, are linked to lower cortisol levels, reducing stress and anxiety.
- Boost Cognitive Function: A healthy gut environment can enhance cognitive functions like memory, focus, and problem-solving.
- Increase Emotional Resilience: A balanced gut microbiome can help with mood swings, irritability, and overall emotional regulation.

To support your mental wellness, try incorporating probiotic and prebiotic-rich foods into your daily diet.
5. The Science Behind Serotonin Production in the Gut
One of the most fascinating discoveries in gut-brain research is that approximately 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut, not the brain. Known as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, serotonin is responsible for regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and cognitive functions.
How Diet Impacts Serotonin Production
Certain foods can help increase serotonin production:
- Tryptophan-Rich Foods: Turkey, eggs, cheese, and tofu contain tryptophan, an amino acid essential for serotonin synthesis.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Whole grains, sweet potatoes, and oats increase serotonin production by making tryptophan more available to the brain.
- Fermented Foods: Probiotic-rich foods improve gut health, which in turn supports serotonin production.

To naturally boost serotonin levels, include foods high in tryptophan and complex carbohydrates in your diet for a balanced mood and improved mental wellness.
6. Common Diets and Their Effects on Mental Health
Different dietary patterns can either support or hinder mental health through the gut-brain axis. Here’s a look at some popular diets and how they affect mental wellness:
- Mediterranean Diet: Known for its high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, the Mediterranean diet has been linked to reduced symptoms of depression. It’s rich in fiber, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties that support both gut and brain health.
- Ketogenic Diet: This low-carb, high-fat diet has shown promise for stabilizing mood by balancing blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, so it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
- Whole-Food, Plant-Based Diet: This diet is packed with fiber, antioxidants, and a variety of nutrients that support gut health. Studies show it can reduce stress, improve mood, and protect against cognitive decline.

Interested in optimizing your mental health through diet? Consider exploring a Mediterranean or plant-based diet for a balanced gut and mind.
7. Tips for Maintaining a Gut-Healthy Diet for Mental Wellness
Transitioning to a gut-healthy diet doesn’t have to be difficult. Here are some simple, effective tips for getting started:
- Include Fiber-Rich Foods Daily: Foods high in fiber, like beans, lentils, and whole grains, feed beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reducing intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats prevents dysbiosis and promotes a balanced gut microbiome.
- Incorporate Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kimchi, and other fermented foods provide probiotics, supporting a healthy gut environment.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for digestion and gut health, so aim for 8–10 cups of water per day.

If you’re ready to improve your mood naturally, try implementing these small but impactful changes in your daily routine.
Conclusion
The gut-brain connection is a powerful reminder that mental health goes beyond the mind—it’s also rooted in our diet and gut health. By eating nutrient-dense, gut-friendly foods, we can nourish both body and brain, fostering better mood stability, cognitive clarity, and emotional resilience.
Take charge of your mental health by making conscious dietary choices. Prioritize gut health, and experience the profound benefits on your mind and mood.
FAQs
- What is the gut-brain connection, and why is it important?
The gut-brain connection is the communication between the gut and the brain, influencing mood and cognitive health. It’s crucial for maintaining mental well-being. - How does diet impact mental health?
Diet affects gut health, which in turn influences neurotransmitter production and mood regulation, underscoring the connection between nutrition and mental wellness. - What are the best foods for supporting the gut-brain axis?
Foods rich in probiotics, prebiotics, fiber, and omega-3 fatty acids are excellent for maintaining a healthy gut-brain connection. - Can probiotics help with anxiety?
Yes, certain probiotics can reduce cortisol levels and balance neurotransmitter production, which helps alleviate anxiety symptoms. - What diet is best for mental health?
The Mediterranean diet, with its high fiber and nutrient content, is widely recognized for supporting mental health through the gut-brain axis.













